TO WATCH CLICK;-https://youtu.be/g_ZqB7ovK-I
The Dark Side of the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War had a profound and lasting impact on the country, and while it devastated much of Vietnam, the nation's recovery and development over the years are remarkable. Let’s explore both sides:
The dark consequences of the war and Vietnam’s journey toward revival. The Dark Side of the Vietnam War Human Suffering and Casualties: The Vietnam War (1955-1975) resulted in millions of deaths. Estimates suggest between 2 to 3 million Vietnamese civilians and soldiers died, along with tens of thousands of American soldiers. Entire villages were destroyed, displacing millions of people.
The psychological trauma of war affected not only those directly involved but future generations as well. Environmental Destruction: The U.S. military’s use of chemical defoliants, particularly Agent Orange, caused catastrophic damage. Approximately 19 million gallons of Agent Orange were sprayed over forests, farmlands, and water bodies. This chemical exposure has led to a rise in cancer, birth defects, and various health issues among Vietnamese people, even decades after the war ended. Economic Devastation: Vietnam’s economy was shattered by the war. Agricultural lands were ruined, industries were destroyed, and poverty became widespread.

AGENT ORANGE
The country struggled with severe food shortages and an almost complete lack of infrastructure. Landmines and Unexploded Ordnance (UXO): Millions of landmines and unexploded bombs were left scattered across the country. This continues to pose risks to civilians, especially in rural areas where agriculture and construction projects often uncover these deadly remnants. Vietnam's Development and Revival Economic Reform (Đổi Mới): In 1986, Vietnam launched its economic reform program called Đổi Mới. This marked a shift from a centrally planned economy to a more market-oriented one.
VIETNAM SIDE OF LIGHT
The country opened up to foreign investment, promoting exports and modernizing its industries. As a result, Vietnam experienced rapid economic growth, transitioning from one of the world’s poorest nations to a lower middle-income country. Major cities like Ho Chi Minh City and Hanoi have undergone significant modernization. Agricultural Success: Post-war Vietnam suffered from food shortages, but the country has since become one of the world’s largest exporters of rice, coffee, and seafood. Improvements in irrigation, land reform, and agricultural policy have allowed Vietnam to become a major player in global food markets, and the agricultural sector now provides stable livelihoods for millions.
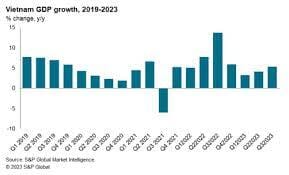
GDP GROWTH OF 2019-2023
Tourism Growth: Vietnam's rich cultural heritage, combined with its natural beauty, has led to a boom in tourism. Places like Ha Long Bay, the ancient town of Hoi An, and historical war sites attract millions of visitors annually, helping boost the economy. War-related tourism, such as tours of the Cu Chi Tunnels and museums, has allowed the country to both preserve its history and educate the world about the lasting impact of the war. Technological and Industrial Development: Vietnam is now an emerging hub for technology and manufacturing. Companies like Samsung, Intel, and Apple have set up factories in the country, turning Vietnam into a major electronics manufacturing center in Southeast Asia. Industrial zones are thriving, and the country is well on its way to becoming a regional powerhouse in sectors like textiles, electronics, and machinery.

TOURISTS IN VIETNAM
Social Progress: Vietnam has made significant strides in education, healthcare, and poverty reduction. The literacy rate is one of the highest in the region, and healthcare services have improved tremendously. Efforts to remove landmines and UXOs have accelerated, with both government initiatives and international assistance helping to clear large areas for safe habitation and farming. Balancing the Legacy of War with Future Development While Vietnam still struggles with the lingering effects of the war, including health issues from Agent Orange and unexploded ordnance, the country has managed to transform its war-torn past into a vibrant future. Development is visible across the nation, and the resilience of the Vietnamese people stands as a testament to their strength.
Technological and Industrial Development:
Vietnam is now an emerging hub for technology and manufacturing. Companies like Samsung, Intel, and Apple have set up factories in the country, turning Vietnam into a major electronics manufacturing center in Southeast Asia.
Industrial zones are thriving, and the country is well on its way to becoming a regional powerhouse in sectors like textiles, electronics, and machinery.

VINBUS ELECTRIC LAUNCHED IN VIETNAM
Balancing the Legacy of War with Future Development
While Vietnam still struggles with the lingering effects of the war, including health issues from Agent Orange and unexploded ordnance, the country has managed to transform its war-torn past into a vibrant future. Development is visible across the nation, and the resilience of the Vietnamese people stands as a testament to their strength.
This balance between remembering the war’s dark legacy and moving toward prosperity defines modern Vietnam, making it one of the most inspiring examples of post-conflict recovery in the world.
Today, Vietnam stands as one of the fastest-growing economies in Southeast Asia, transforming from a war-torn country into a dynamic player on the global stage. Key areas of its development include economic growth, industrial expansion, infrastructure improvement, and social progress.
1. Economic Growth and Reforms
Strong GDP Growth: Vietnam has maintained a high GDP growth rate, averaging around 6-7% annually in recent years, making it one of the most vibrant economies in the region.
Đổi Mới Reforms: Since launching the Đổi Mới (renovation) reforms in 1986, Vietnam shifted from a centrally planned economy to a more market-oriented one. These reforms opened the country to foreign investment, trade, and private enterprise.
Diversification of Industries: Vietnam's economy has diversified into various sectors, including manufacturing, technology, agriculture, and services. It has become a key hub for electronics manufacturing, with major companies like Samsung, Apple, and Intel establishing operations there.
2. Industrial and Technological Advancement
Manufacturing Powerhouse: Vietnam has become a global manufacturing center, particularly in electronics, textiles, footwear, and machinery. The country’s labor force, cost competitiveness, and political stability have attracted significant foreign direct investment (FDI).
Technology Growth: Vietnam is making strides in developing its technology sector, with a growing tech-savvy workforce. The government has prioritized digital transformation and innovation, making the country an emerging hub for startups, particularly in fintech and e-commerce.
Green Energy Initiatives: In response to global climate challenges, Vietnam is investing in renewable energy projects, particularly solar and wind power, positioning itself as a leader in clean energy transition in the region.
3. Infrastructure and Urban Development
Transportation and Connectivity: Vietnam has made significant investments in upgrading its infrastructure, including roads, airports, and ports. Projects like the North-South Expressway and expansions of major ports in cities like Ho Chi Minh City and Hai Phong have boosted the country’s connectivity, both domestically and internationally.
Urbanization: Cities like Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City have seen rapid urbanization, with modern skyscrapers, shopping malls, and improved public transportation systems. These urban centers are becoming vibrant hubs for business, tourism, and international trade.
Poverty Reduction: Vietnam has made remarkable progress in reducing poverty. Since the 1990s, millions of people have been lifted out of poverty, and the country now enjoys a relatively low poverty rate, thanks to economic growth and social policies.
Education and Healthcare: Vietnam boasts one of the highest literacy rates in Southeast Asia, with strong investments in education. The healthcare system has also improved, with efforts to make services more accessible and affordable to the population.
Workforce Development: The government has placed a strong emphasis on developing a skilled workforce through vocational training, technical education, and partnerships with international institutions to prepare for the demands of an evolving economy.
5. Foreign Relations and Global Integration
Trade Agreements: Vietnam has signed numerous trade agreements, including the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) and the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP). These agreements have opened new markets for Vietnamese goods and deepened the country's integration into the global economy.
Strategic Diplomacy: Vietnam has strengthened its diplomatic ties with major powers, balancing relations with the U.S., China, and ASEAN countries. Its foreign policy focuses on economic cooperation, maintaining peace, and regional stability in the South China Sea.
6. Tourism Growth
Cultural and Natural Attractions: Vietnam continues to be a top destination for international tourists, with places like Ha Long Bay, Hoi An, and the Mekong Delta attracting millions of visitors. The tourism sector has become a significant contributor to the country’s economy.
War Remnants and Historical Sites: Many tourists visit Vietnam to explore its history, particularly the Vietnam War. Museums, battle sites, and places like the Cu Chi Tunnels offer insights into the country’s past, while also supporting its modern tourism industry.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Sustainability: Vietnam faces environmental challenges, including pollution and climate change, particularly rising sea levels threatening the Mekong Delta. The country is working toward greener policies but still faces hurdles in balancing rapid industrialization with environmental protection.
Income Inequality: While poverty has decreased, income inequality between urban and rural areas persists. The government is focusing on reducing this gap through rural development and social welfare programs.
